Ford Explorer: Voltage Converter/Inverter / Description and Operation - Direct Current/Direct Current (DC/DC) Converter Control Module - System Operation and Component Description
System Operation
System Diagram - DCDC
.jpg)
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ignition Switch |
| 2 | PCM |
| 3 | SOBDMC |
| 4 | BCM |
| 5 | BECM |
| 6 | DCDC |
| 7 | High Voltage/Low Current Fuse |
| 8 | 12V Battery Monitoring Sensor |
Network Message Chart
DCDC Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
| DCDC HEV wake up enable | BECM, BCCM (battery charger control module) ( PHEV only) | Command to enable the DCDC |
| DCDC HEV wake up enable | SOBDMC | Hard wired command to enable the DCDC |
| High voltage input | SOBDMC | Voltage measured at SOBDMC used to compare with voltage at the DCDC. |
| Power pack torque status | PCM | Determines if the power pack is on or off and if torque is available. |
| Gear lever position | PCM | Determines the transaxle gear state. |
| DCDC low setpoint request | PCM | Enables and sets the low voltage charging setpoint. |
| OBDII warm up completions | PCM | Counter for DTC aging. |
| Ambient air temperature | PCM | Ambient air temperature measured. |
| High voltage battery status | BECM | High voltage battery current flow, contactor commands and system shutdown status. |
| Power mode status | BCM | Information of current power mode state. |
| Ignition status | BCM | Determines the ignition state. |
| 12-volt battery sensor voltage (gateway) | BCM | 12-volt battery voltage measured with battery sensor. |
| Vehicle configuration data (gateway) | BCM | Vehicle configuration strategy. |
DCDC Operation
The DCDC is responsible for maintaining and charging the 12-volt battery. The SOBDMC sends a HEV wakeup signal to the DCDC through a hardwired circuit. For information on the high-voltage battery system,
Refer to: High Voltage Battery, Mounting and Cables - System Operation and Component Description (414-03 High Voltage Battery, Mounting and Cables, Description and Operation).
The DCDC
is liquid cooled by the electric motor cooling system circuit. The
electric motor cooling circuit uses an electric motor diverter valve
that acts as a system thermostat, allowing the coolant to flow within
the motor circuit while the motor warms. As the coolant warms, the
diverter valve slowly opens to allow coolant flow to the radiator. For
more information on electric powertrain cooling,
Refer to: Electric Powertrain Cooling - Overview (303-03E Electric Powertrain Cooling - 3.3L Duratec-V6 – Hybrid (BP), Description and Operation).
The DCDC communicates on the HS-CAN1 with or without the high voltage contactors closed. A wake up circuit from the SOBDMC activates the module processor. If the wake up circuit fails and high-voltage is present, the DCDC still charges but with a delay.
Faults with the DCDC that cause low or excessively high 12-volt battery voltage result in the DCDC sending a network message requesting the CHECK CHARGING SYSTEM message be displayed in the message center.
The DCDC is protected by a 30 amp high voltage low current fuse located in the high-voltage BJB. The DCDC steps the high-voltage down to a low-voltage (between 13.0 and 15.5 volts, depending on vehicle needs), providing power to the vehicle low-voltage battery systems. Depending on the vehicle and environmental conditions, the DCDC is capable of outputting as many as 165 amps to the 12-volt battery.
Component Description
DCDC
The DCDC is responsible for maintaining and charging the 12-volt battery, it communicates on the HS-CAN1.
SOBDMC
The SOBDMC provides a wake up signal to the DCDC during key on.
PCM
The PCM communicates on the HS-CAN1 and determines the ambient air temperature, enables and sets the low voltage charging setpoint, determines power pack status and transaxle gear state.
BECM
The BECM communicates on the HS-CAN1, determines the high voltage battery current flow, commands the high voltage contactors and monitors system shutdown status.
BCM
The BCM communicates on the HS-CAN1, determines the ignition state, communicates the power mode state and measures the 12-volt battery voltage with the battery sensor.
 Description and Operation - Direct Current/Direct Current (DC/DC) Converter Control Module - Overview
Description and Operation - Direct Current/Direct Current (DC/DC) Converter Control Module - Overview
OVERVIEW
WARNING:
To prevent the risk of high-voltage shock, always follow
precisely all warnings and service instructions, including instructions
to depower the system...
Other information:
Ford Explorer 2020-2025 Service Manual: General Procedures - Power Liftgate Initialization
Initialization Disconnect the battery or remove the RGTM fuse(s). Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures). NOTE: Remove the battery power from the RGTM for 20 seconds before entering initialization mode...
Ford Explorer 2020-2025 Service Manual: General Procedures - Wheel to Hub Runout Minimization
Check NOTE: Wheel-to-hub optimization is important. Clearance between the wheel and hub can be used to offset or neutralize the Road Force® or run-out of the wheel and tire assembly. For every 0.001 inch of wheel-to-hub clearance, the Road Force® can be affected between 1 and 3 pounds depending on the tire stiffness...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 6th Generation Explorer Owners Manual
- 6th Generation Explorer Service Manual
- General Procedures - Rear Camber Adjustment
- Traction Control
- Auxiliary Power Points
- New on site
- Most important about car
Gauges
4 Inch Display
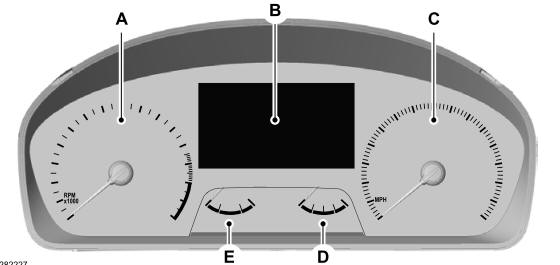
A - Tachometer.
B - Information display.
C - Speedometer.
D - Fuel gauge.
E - Engine coolant temperature gauge.

.jpg)
